https://www.drax.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Drax-2021-HYR-Analyst-Presentation.pdf
Tag: investors
Half year results for the six months ended 30 June 2021 [PDF]
https://www.drax.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Drax-H1-results-2021-6-months-ended-30-June.pdf
Half year results for the six months ended 30 June 2021

RNS Number: 8333G
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
| Six months ended 30 June | H1 2021 | H1 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Key financial performance measures | ||
| Adjusted EBITDA (£ million)(1)(2) | 186 | 179 |
| Continuing operations | 165 | 160 |
| Discontinued operations – gas generation | 21 | 19 |
| Net debt (£ million)(3) | 1,029 | 792 |
| Adjusted basic EPS (pence)(1) | 14.6 | 10.8 |
| Interim dividend (pence per share) | 7.5 | 6.8 |
| Total financial performance measures from continuing operations | ||
| Operating profit / (loss) (£ million) | 84 | (57) |
| Profit / (loss) before tax (£ million) | 52 | (85) |
Will Gardiner, CEO of Drax Group, said:
“We have had a great first half of the year, transforming Drax into the world’s leading sustainable biomass generation and supply company as well as the UK’s largest generator of renewable power.
“The business has performed well, and we have exciting growth opportunities to support the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
“Drax has reduced its generation emissions by over 90%, and we are very proud to be one of the lowest carbon intensity power generators in Europe – a huge transformation for a business which less than a decade ago operated the largest coal power station in Western Europe.
“In the past six months we have significantly advanced our plans for Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) in the UK and globally. By 2030 Drax could be delivering millions of tonnes of negative emissions and leading the world in providing a critical technology needed to tackle the climate crisis.
“We are pleased to be announcing a 10% increase in our dividend, and we remain committed to creating long-term value for all our stakeholders.”
Financial highlights
- Adjusted EBITDA from continuing and discontinued operations up £7 million to £186 million (H1 2020: £179 million)
- Acquisition of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc. (Pinnacle) for cash consideration of C$385 million (£222 million) (enterprise value of C$796 million) and sale of gas generation assets for £186 million
- Strong liquidity and balance sheet
- £666 million of cash and committed facilities at 30 June 2021
- Refinancing of Canadian facilities (July 2021) with lower cost ESG facility following Pinnacle acquisition
- Sustainable and growing dividend – expected full year dividend up 10% to 18.8 pence per share (2020: 17.1p/share)
- Interim dividend of 7.5 pence per share (H1 2020: 6.8p/share) – 40% of full year expectation
Strategic highlights
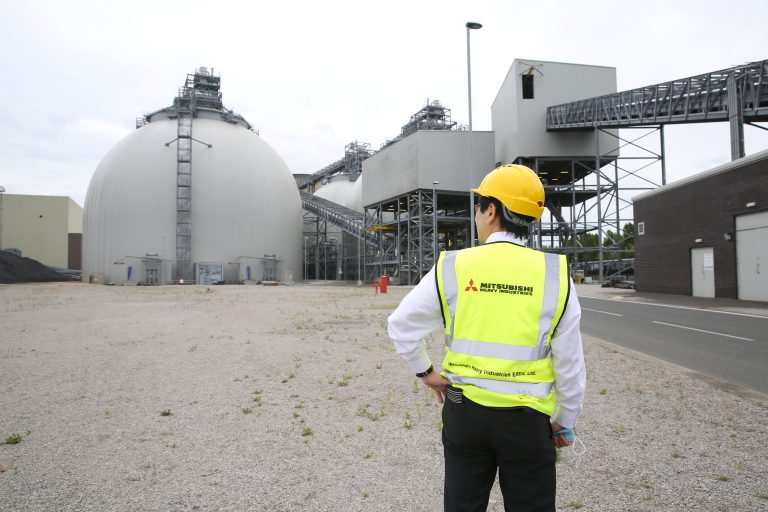

Kentaro Hosomi, Chief Regional Officer EMEA, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) at Drax Power Station, North Yorkshire
- Developing complementary biomass strategies for supply, negative emissions and renewable power
- Creation of the world’s leading sustainable biomass generation and supply company
- Supply – 17 operational plants and developments across three major fibre baskets with production capacity of 4.9Mt pa and $4.3 billion of long-term contracted sales to high-quality customers in Asia and Europe
- Generation – 2.6GW of biomass generation – UK’s largest source of renewable power by output
- >90% reduction in generation emissions since 2012
- Sale of gas generation assets January 2021 and end of commercial coal March 2021
- Development of BECCS
- Planning application submitted for Drax Power Station and technology partner (MHI) selected
- Participation in East Coast Cluster – phase 1 regional clusters and projects to be selected from late 2021
- Partnerships with Bechtel and Phoenix BioPower evaluating international BECCS and biomass technologies
- System support – option to develop Cruachan from 400MW to over 1GW – commenced planning approval process
Outlook
- Adjusted EBITDA, inclusive of Pinnacle from 13 April 2021, full year expectations unchanged
Operational review
Pellet Production – acquisition of Pinnacle, capacity expansion and biomass cost reduction
- Sustainable sourcing
- Biomass produced using forestry residuals and material otherwise uneconomic to commercial forestry
- Science-based sustainability policy fully compliant with current UK, EU law on sustainable sourcing aligned with UN guidelines for carbon accounting
- All woody biomass verified and audited against FSC®(4), PEFC or SBP requirements
- Adjusted EBITDA (including Pinnacle since 13 April 2021) up 60% to £40 million (H1 2020: £25 million)
- Pellet production up 70% to 1.3Mt (H1 2020: 0.8Mt)
- Cost of production down 8% to $141/t(5) (H1 2020: $154/t(5))
- Near-term developments in US Southeast (2021-22)
- Commissioning of LaSalle expansion, Demopolis and first satellite plant in H2
- Other opportunities for growth and cost reduction
- Increased production capacity, supply of biomass to third parties and expansion of fuel envelope to include lower cost biomass
Generation – flexible and renewable generation
- 12% of UK’s renewable electricity, strong operational performance and system support services
- Adjusted EBITDA down 14% to £185 million (H1 2020: £214 million)
- Biomass – Lower achieved power prices and higher GBP cost of biomass reflecting historical power and FX hedging
- Strong system support (balancing mechanism, Ancillary Services and optimisation) of £70 million (H1 2020: £66 million) – additional coal operations and continued good hydro and pumped storage performance, in addition to coal operations
- Coal – utilisation of residual coal stock in Q1 2021 and capture of higher power prices
Pumped storage / hydro – good operational and system support performance
- £34 million of Adjusted EBITDA (Cruachan, Lanark, Galloway schemes and Daldowie) (H1 2020: £35 million)
- Ongoing cost reductions to support operating model for biomass at Drax Power Station from 2027
- End of commercial coal operations in March, formal closure September 2022 – reduction in fixed cost base
- Major planned outage for biomass CfD unit – August to November 2021 – including third turbine upgrade delivering improved thermal efficiency and lower maintenance cost, supporting lower cost biomass operations
- Trials to expand range of lower cost biomass fuels – up to 35% load achieved in test runs on one unit
- Strong contracted power position – 29.3TWh sold forward at £52.1/MWh 2021-2023. Opportunities to capture higher power prices in future periods, subject to liquidity
| As at 25 July 2021 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed price power sales (TWh) | 15.9 | 9.1 | 4.3 | |
| - CfD(6) | 3.8 | 0.6 | - | |
| - ROC | 10.8 | 8.4 | 4.0 | |
| - Other | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | |
| At an average achieved price (£ per MWh) | 51.7 | 52.4 | 52.7 |
Customers – renewable electricity and services under long-term contracts to high-quality I&C customer base
- Adjusted EBITDA loss of £5 million inclusive of £10-15 million impact of Covid-19 (H1 2020 £37 million loss inclusive of £44 million impact of Covid-19)
- Continuing development of Industrial & Commercial (I&C) portfolio
- Focusing on key sectors to increase sales to high-quality counterparties supporting generation route to market
- Energy services expand the Group’s system support capability and customer sustainability objectives
- Closure of Oxford and Cardiff offices as part of SME strategic review and the rebranding of the Haven Power I&C business to Drax
- Continue to evaluate options for SME portfolio to maximise value and alignment with strategy
Other financial information
- Total operating profit from continuing operations of £84 million including £20 million mark-to-market gain on derivative contracts and acquisition related costs of £10 million and restructuring costs of £2 million
- Total loss after tax from continuing operations of £6 million including a £48 million charge from revaluing deferred tax balances following announcement of future UK tax rate changes
- Total loss after tax from continuing operations of £6 million including a £48 million charge from revaluing deferred tax balances following confirmation of UK corporation tax rate increases from 2023
- Capital investment of £71 million (H1 2020: £78 million) – continued investment in biomass strategy
- Full year expectation of £210–230 million, includes pellet plant developments – LaSalle expansion, satellite plants and commissioning of Demopolis
- Group cost of debt now below 3.5% reflecting refinancing of Canadian facilities in July 2021
- Net debt of £1,029 million (31 December 2020: £776 million), including cash and cash equivalents of £406 million (31 December 2020: £290 million)
- 5x net debt to Adjusted EBITDA, with £666 million of total cash and committed facilities (31 December 2020: £682 million)
- Continue to expect around 2.0x net debt to Adjusted EBITDA by end of 2022
| View complete half year report | View investor presentation | Listen to webcast |
Notice of half year results announcement

RNS Number: 1115G
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
Drax Group plc (“Drax”) confirms that it will be announcing its Half Year Results for the six months ended 30 June 2021 on Thursday 29 July 2021.
Information regarding the results presentation and webcast is detailed below.
Results presentation and webcast arrangements
Management will host a webcast presentation for analysts and investors at 9:00am (UK Time), Thursday 29 July 2021.
The presentation can be accessed remotely via a live webcast link, as detailed below. After the meeting, the webcast recording will be made available and access details of this recording are also set out below.
A copy of the presentation will be made available from 7:00am (UK time) on Wednesday 29 July 2021 for download at: www.drax.com/investors/announcements-events-reports/presentations/
Event Title:
Drax Group plc: Half Year Results
Event Date:
Thursday 29 July 2021
9:00am (UK time)
Webcast Live Event Link:
https://secure.emincote.com/client/drax/drax015
Conference call and pre-register Link:
https://secure.emincote.com/client/drax/drax015/vip_connect
Start Date:
Thursday 29 July 2021
Delete Date:
Thursday 31 December 2021
Archive Link:
https://secure.emincote.com/client/drax/drax015
For further information, please contact:
Website: www.Drax.com
Refinancing of Pinnacle Debt with Lower Cost ESG Facility

RNS Number: 9930E
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
Drax is pleased to announce that it has completed the refinancing of the Canadian dollar facilities it acquired as part of the Group’s acquisition of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc. (Pinnacle) in April 2021.
The new C$300 million term facility (“the Facility”) matures in 2024, with an option to extend by two years(1), and has a customary margin grid referenced over CDOR(2).

A Pinnacle wood pellet plant
The Facility reduces further the Group’s all-in cost of debt to below 3.5% and includes an embedded ESG component which adjusts the margin payable based on Drax’s carbon intensity measured against an annual benchmark.
The Facility, along with surplus cash, replaces Pinnacle’s approximately C$435 million facilities which had a cost of over 5.5%.
Enquiries
Drax Investor Relations: Mark Strafford
Media
Drax External Communications: Ali Lewis
Website: www.Drax.com
END
How to build a business model for negative emissions

In brief
-
Policy intervention is needed to enable enough BECCS in power to make a net zero UK economy possible by 2050
-
Early investment in BECCS can insure against the risk and cost of delaying significant abatement efforts into the 2030s and 2040s
-
A two-part business model for BECCS of carbon payment and power CfD offers a clear path to technology neutral and subsidy free GGRs
The UK’s electricity system is based on a market of buying and selling power and other services. For this to work electricity must be affordable to consumers, but the parties providing power must be able to cover the costs of generating electricity, emitting carbon dioxide (CO2) and getting electricity to where it needs to be.
This process has thrived and proved adaptable enough to rapidly decarbonise the electricity system in the space of a decade.
With a 58% reduction in the carbon intensity of power generation, the UK’s electricity has decarbonised twice as fast as that of other major economies. As the UK pushes towards its goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2050, new technologies are needed, and the market must extend to enable innovation.
Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is one of the key technologies needed at scale for the UK to reach net zero. Yet there is no market for the negative emissions BECCS can deliver, in contrast to other energy system services.
BECCS has been repeatedly flagged as vital for the UK to reach its climate goals, owing to its ability to deliver negative emissions. The Climate Change Committee has demonstrated that negative emissions – also known as greenhouse gas removals (GGRs) or carbon removals – will be needed at scale to achieve net zero, to offset residual emissions from hard to decarbonise sectors such as aviation and agriculture. But there is no economic mechanism to reward negative emissions in the energy market.
For decarbonisation technologies like BECCS in power to develop to the scale and within the timeframe needed, the Government must implement the necessary policies to incentivise investment, and allow them to thrive as part of the energy and carbon markets.
BECCS is essential to bringing the whole economy to net zero
The primary benefit of BECCS in power is its ability to deliver negative emissions by removing CO2 from the atmosphere through responsibly managed forests, energy crops or agricultural residues, then storing the same amount of CO2 underground, while producing reliable, renewable electricity.

Looking down above units one through five within Drax Power Station
A new report by Frontier Economics for Drax highlights BECCS as a necessary cornerstone of UK decarbonisation and its wider impacts on a net zero economy. Developing a first-of-a-kind BECCS power plant would have ‘positive spillover’ effects that contribute to wider decarbonisation, green growth and the UK’s ability to meet its legally-binding climate commitments by 2050.
Drax has a unique opportunity to fit carbon capture and storage (CCS) equipment to its existing biomass generation units, to turn its North Yorkshire site into what could be the world’s first carbon negative power station.
Plans are underway to build a CO2 pipeline in the Yorkshire and Humber region, which would move carbon captured from at Drax out to a safe, long-term storage site deep below the North Sea. This infrastructure would be shared with other CCS projects in the Zero Carbon Humber partnership, enabling the UK’s most carbon-intensive region to become the world’s first net zero industrial cluster.
Developing BECCS can also have spillover benefits for other emerging industries. Lessons that come from developing and operating the first BECCS power stations, as well as transport and storage infrastructure, will reduce the cost of subsequent BECCS, negative emissions and other CCS projects.
Hydrogen production, for example, is regarded as a key to providing low, zero or carbon negative alternatives to natural gas in power, industry, transport and heating. Learnings from increased bioenergy usage in BECCS can help develop biomass gasification as a means of hydrogen production, as well as applying CCS to other production methods.
The economic value of these positive spillovers from BECCS can be far reaching, but they will not be felt unless BECCS can achieve a robust business model in the immediate future.
With a 58% reduction in the carbon intensity of power generation, the UK’s electricity has decarbonised twice as fast as that of other major economies. As the UK pushes towards its goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2050, new technologies are needed, and the market must extend to enable innovation.
Designing a BECCS business model
The Department for Business Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) outlined several key factors to consider in assessing how to make carbon capture, usage and storage (CCUS) economically viable. These are also valid for BECCS development.

Engineers working within the turbine hall, Drax Power Station
One of the primary needs for a BECCS business model is to instil confidence in investors – by creating a policy framework that encourages investors to back innovative new technologies, reduces risk and inspires new entrants into the space. The cost of developing a BECCS project should also be fairly distributed among contributing parties ensuring that costs to consumers/taxpayers are minimised.
Building from these principles there are three potential business models that can enable BECCS to be developed at the scale and in the timeframe needed to bring the UK to net zero emissions in 2050.
- Power Contract for Difference (CfD):
By protecting consumers from price spikes, and BECCS generators and investors from market volatility or big drops in the wholesale price of power, this approach offers security to invest in new technology. The strike price could also be adjusted to take into account negative emissions delivered and spillover benefits, as well as the cost of power generation. - Carbon payment:
Another approach is contractual fixed carbon payments that would offer a BECCS power station a set payment per tonne of negative emissions which would cover the operational and capital costs of installing carbon capture technology on the power station. This would be a new form of support, and unfamiliar to investors who are already versed in CfDs. The advantage of introducing a policy such as fixed carbon payment is its flexibility, and it could be used to support other methods of GGR or CCS. The same scheme could be adjusted to reward, for example, CO2 captured through CCS in industry or direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS). It could even be used to remunerate measurable spillover benefits from front-running BECCS projects. - Carbon payment + power CfD:
This option combines the two above. The Frontier report says it would be the most effective business model for supporting a BECCS in power project. Carbon payments would act as an incentive for negative emissions and spillovers, while CfDs would then cover the costs of power generation.
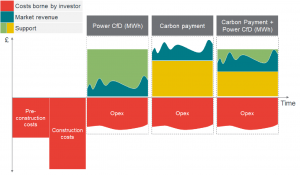
Cost and revenue profiles of alternative support options based on assuming a constant level of output over time.
Way to go, hybrid!
Why does the hybrid business model of power CfD with carbon payment come out on top? Frontier considered how easy or difficult it would be to transition each of the options to a technology neutral business model for future projects, and then to a subsidy free business model.
By looking ahead to tech neutrality, the business model would not unduly favour negative emissions technologies – such as BECCS at Drax – that are available to deploy at scale in the 2020s, over those that might come online later.
Plus, the whole point of subsidies is to help to get essential, fledgling technologies and business models off to a flying start until the point they can stand on their own two feet.
The report concluded:
- Ease of transition to technology neutrality: all three options are unlikely to have any technology neutral elements in the short-term, although they could transition to a mid-term regime which could be technology neutral; and
- Ease of transition to subsidy free: while all of the options can transition to a subsidy free system, the power CfD does not create any policy learnings around treatment of negative emissions that contribute to this transition. The other two options do create learnings around a carbon payment for negative emissions that can eventually be broadened to other GGRs and then captured within an efficient CO2 market.
‘Overall, we conclude that the two-part business model performs best on this criterion. The other two options perform less well, with the power CfD performing worst as it does not deliver learnings around remunerating negative emissions.’
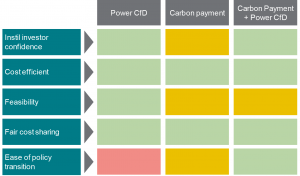
Assessment of business model options. Green indicates that the criteria is largely met, yellow indicates that it is partially met, and red indicates that it is not met.
Transition to a net zero future
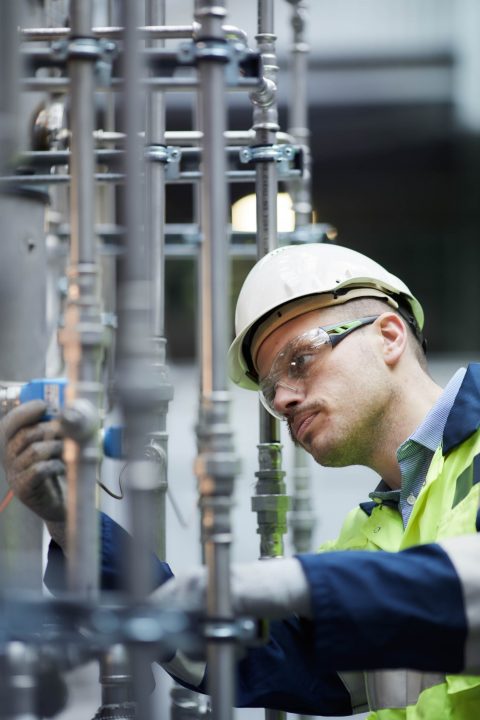

Engineer inspects carbon capture pilot plant at Drax Power Station
Crucial to the implementation of BECCS is the feasibility of these business models, in terms of their practicality in being understood by investors, how quickly they can be put into action and how they will evolve or be replaced in the long-term as technologies mature and costs go down. This can be improved by using models that are comparable with existing policies.
These business models can only deliver BECCS in power (as well as other negative emissions technologies) at scale and enable the UK to reach its 2050 net zero target, if they are implemented now.
Every year of stalling delays the impact positive spillovers and negative emissions can have on global CO2 levels. The UK Government must provide the private sector with the confidence to deliver BECCS and other net zero technologies in the time frame needed.
Go deeper
Explore the Frontier Economics report for Drax, ‘Supporting the deployment of Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) in the UK: business model options.’
Robust trading and operational performance in Q1-2021, progressing biomass strategy
RNS Number : 0962W
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
Highlights
- Robust trading and operational performance during the first three months of 2021
- Completion of acquisition of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc. (Pinnacle)
- Strong balance sheet and cash flows
- Continue to expect net debt to Adjusted EBITDA(1) of around 2 x by the end of 2022
- Continued focus on clean energy generation and a reduction in carbon emissions
- Commercial coal generation ended in March 2021, with full closure in September 2022
- Sale of existing gas generation assets in January 2021
- Sustainable and growing dividend
- Final dividend of 10.3 pence per share – subject to shareholder approval at AGM
- Total dividends of 17.1 pence per share, 7.5% y-o-y growth
Will Gardiner, Drax Group CEO, said:
“In the first quarter of 2021 we delivered a robust trading and operational performance, alongside steps to further decarbonise the business and support our flexible and renewable generation strategy. These include the end of commercial coal generation, the sale of our gas power stations and just last week we acquired leading Canadian biomass producer Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc.
“The acquisition of Pinnacle positions Drax as the world’s leading sustainable biomass generation and supply business. This advances our strategy to increase self-supply, reduce our own cost of biomass production and create a long-term future for sustainable bioenergy, which will pave the way for the development of negative emissions from Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS). BECCS at Drax would make a significant contribution to the UK reaching its new target to cut carbon emissions by 78% by 2035.”
Trading, operational performance and outlook
The trading and operational performance of the Group has been robust in the first three months of 2021. Full year expectations for the Group remain underpinned by continued good operational availability for the remainder of 2021.
Generation
Drax’s generation portfolio has performed well with good asset availability and optimisation across its portfolio, including a strong system support performance from Cruachan (pumped storage), underpinning a solid financial performance.
During the summer Drax will, as previously announced, undertake planned maintenance on its CfD(2) biomass unit, including a high-pressure turbine upgrade to reduce maintenance costs and improve thermal efficiency, contributing to lower generation costs for Drax Power Station.
In March 2021 Drax secured Capacity Market agreements for its hydro and pumped storage assets worth around £10 million for the delivery period October 2024 to September 2025.
Drax also secured 15-year agreements for three new 299MW system support Open Cycle Gas Turbine (OCGT) projects in England and Wales. As the UK transitions towards a net zero economy it will become increasingly dependent on intermittent renewable generation. As such, fast response system support technologies, such as these OCGTs, are increasingly important in enabling the UK energy system to run more frequently and securely on intermittent renewable generation. Drax is continuing to evaluate options for these projects including their potential sale.
Pellet Production
Pellet Production has performed well with good production and cost reduction plans on track.
On 13 April 2021, Drax completed its acquisition of Pinnacle. The acquisition advances the Group’s biomass strategy by more than doubling its sustainable biomass production capacity, significantly reducing its cost of production and adding a major biomass supply business, underpinned by long-term third-party supply contracts.
The Group’s enlarged supply chain will have access to 4.9 million tonnes of operational capacity from 2022. Of this total, 2.9 million tonnes are available for Drax’s self-supply requirements in 2022 (increasing to 3.4 million tonnes in 2027).
The acquisition positions Drax as the world’s leading sustainable biomass generation and supply business alongside the continued development of its ambition to be a carbon negative company by 2030, using BECCS.
Pinnacle’s performance in the first three months of 2021 was in line with Drax’s expectations through the acquisition process. Drax will update on full year expectations including Pinnacle at its half year results on 29 July 2021.
Customers
The Group’s I&C(3) supply business performed well. It continues to provide a route to market for Drax’s power and renewable products to high credit quality counterparties as well as opportunities to complement the Group’s system support capabilities.
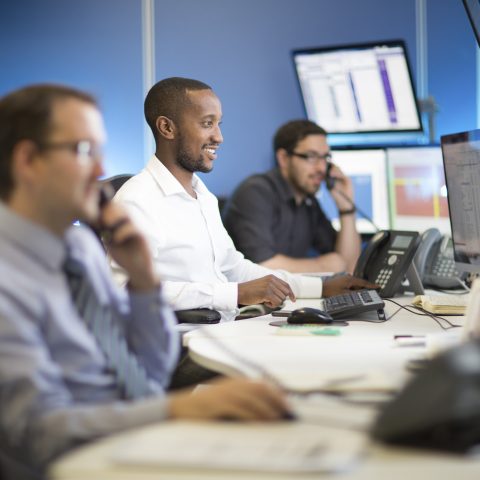

Trading desk at Haven Power, Ipswich
The SME(4) supply business continued to be affected by the ongoing Covid-19 restrictions in the first three months of 2021. Drax is continuing to explore operational and strategic options for this segment of the business.
Balance sheet
As at 31 March 2021, Drax had cash and total committed facilities of £801 million.
Drax will retain Pinnacle’s existing debt facilities within the enlarged Group’s capital structure but will consider opportunities to optimise its balance sheet with lower cost sources of debt.
Drax continues to expect net debt to Adjusted EBITDA to return to its long-term target of around 2 x by the end of 2022.
Generation contracted power sales
As at 16 April 2021, Drax had 25.7TWh of power sales contracted at £49.0/MWh as follows:
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed price power sales (TWh) | 15.0 | 7.5 | 3.2 |
| Contracted % versus 2020 full year output (5) | 101% | 51% | 22% |
| Of which CfD (TWh) (6) | 3.2 | - | - |
| At an average achieved price (£ per MWh) | 49.2 | 48.6 | 49 |
Capital allocation and dividend
The Group remains committed to the capital allocation policy established in 2017, through which it aims to maintain a strong balance sheet; invest in the core business; pay a sustainable and growing dividend and return surplus capital beyond investment requirements to shareholders.
A final 2020 dividend of 10.3 pence per share was proposed in the 2020 results on 25 February 2021 and, subject to shareholder approval at today’s Annual General Meeting, will be paid on 14 May 2021.
An interim dividend of 6.8 pence per share was paid on 2 October 2020, making the total 2020 dividend 17.1 pence per share, an increase of 7.5% compared to 2019.
Enquiries:
Drax Investor Relations: Mark Strafford
Media:
Drax External Communications: Ali Lewis
Website: www.drax.com
END
Completion of the acquisition of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc.

RNS Number : 2689V
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
Drax is pleased to announce that it has completed the acquisition of the entire issued share capital of Pinnacle Renewable Inc.
The Acquisition was originally announced on 8 February 2021.
Enquiries:
Drax Investor Relations: Mark Strafford
Media:
Drax External Communications: Ali Lewis
Satisfaction / waiver of conditions in relation to the proposed acquisition of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc.

RNS Number : 6420U
Drax Group plc
(“Drax” or the “Group”; Symbol:DRX)
On 8 February 2021, Drax announced that it had entered into an agreement to acquire the entire issued share capital of Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc. (the “Acquisition”). On 31 March 2021, Drax announced that the Acquisition had been approved by Drax Shareholders at the General Meeting and Pinnacle announced that the Acquisition had been approved by Pinnacle Shareholders.
Drax is pleased to announce that on 6 April 2021 the Supreme Court of British Columbia granted the Final Order. All of the conditions to the Completion of the Acquisition have now been satisfied or waived (other than conditions which can only be satisfied at Completion) and Completion is expected to occur on 13 April 2021.
Capitalised terms used but not defined in this announcement have the meanings given to them in the Circular.
Enquiries:
Drax Investor Relations: Mark Strafford
Media:
Drax External Communications: Ali Lewis











