
View here

View here

Electricity systems around the world are decarbonising and increasingly switching to renewable power sources. While intermittent sources, such as solar and wind, are the fastest growing types of renewables being installed globally, the reliability and flexibility of biomass and its ability to offer grid stabilisation services such as frequency control and inertia make it an increasingly necessary source of renewable power. According to the International Energy Agency biomass generation is forecast to expand as planned projects come online.

Biomass comes in many different forms. When looking to assess future demand and use, it is important to recognise benefits that different types of biomass bring. Compressed wood pellets are just one small part of the biomass spectrum, which includes many forms of agricultural and livestock residues, waste and bi-products – much of which is currently discarded or underutilised.
Maximising the use of these wastes and residues provides plenty of scope for expansion of the biomass energy sector around the world. The global installed capacity for biomass generation is expected to reach close to 140 gigawatts (GW) by 2026, which will be fuelled primarily by expansion in Asia using residues from food production and the forestry processing industry.
However, the use of woody biomass can also provide many benefits too, such as supplying a market for thinnings, providing a use for harvesting residues, encouraging better forest management practices and generating increased revenue for forest owners.
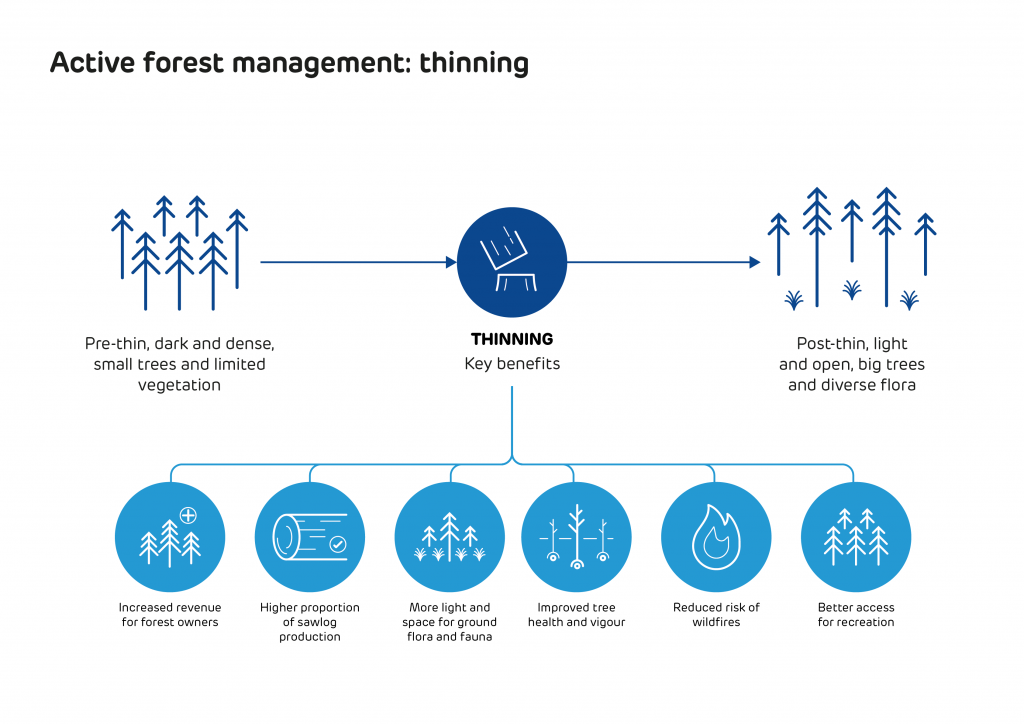
In areas like the US South, traditional markets for forest products have declined, whilst forest growth has significantly increased. According to the USDA Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) data, there is an average annual surplus of growth in the US South of more than 176 million cubic metres compared to removals – that’s enough to make around 84 million tonnes of wood pellets a year, from just one supply region.

Of course, not all of this surplus growth could or should be used for bio-energy, much of it is suitable for high value markets like saw-timber or construction and some of it is located on inaccessible or protected sites. However, new and additional markets are essential to maintain the health of the forest resource and to encourage forest owners to retain and maintain their forest assets.
In the current wood pellet supply regions for Europe, Pöyry management consulting has calculated that there is a surplus of low grade wood fibre and residues that could make an additional 140 million tonnes of wood pellets each year.

Compressed wood pellets on a conveyor belt
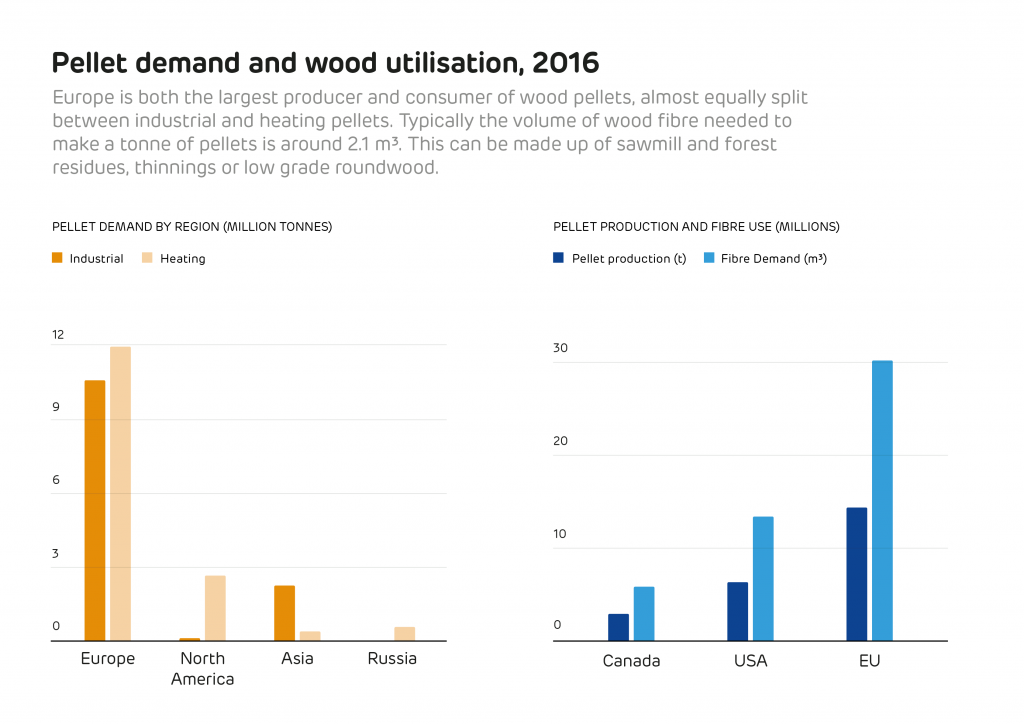
It is also necessary to look at the global production of all wood products to put wood pellet production into context. In 2016 the global production of industrial roundwood (the raw material used for construction, furniture, paper and other wood products) was 1.87 billion cubic metres, while the global production of wood fuel (used for domestic heating and cooking) was 1.86 billion cubic metres[1]. Only around 1.6% of this feedstock was used to make wood pellets, both for industrial energy and residential heat. The total production of wood pellets in 2016 was 28.4 million tonnes, of which only 45% was used for industrial energy[2].
While Forestry consulting and research firm Forisk predicts demand for industrial wood pellets (those used in electricity generation rather than residential heating) will grow globally at an annual rate of 15% for the next five years, reaching 27.5 megatonnes (Mt) by 2023, they are also clear that this growth, in context, will not impact forest volumes or other markets:
‘The wood pellet industry in the US South is not exploding, it is a tiny component of the overall market. Forest volumes in the South in total will continue to grow for decades no matter what bioenergy markets or housing markets do. The wood pellet sector simply and unequivocally cannot compete economically with US pulp and paper mills (80% of pulpwood demand in South) for raw material on a head-to-head basis[3].’
So, while demand for wood pellets is likely to increase over the next 10 years, this increase will be well within the scope of existing surplus fibre. The question, therefore, is can suppliers keep up with this demand? And can they do this while ensuring it remains sustainable, reliable and renewable?
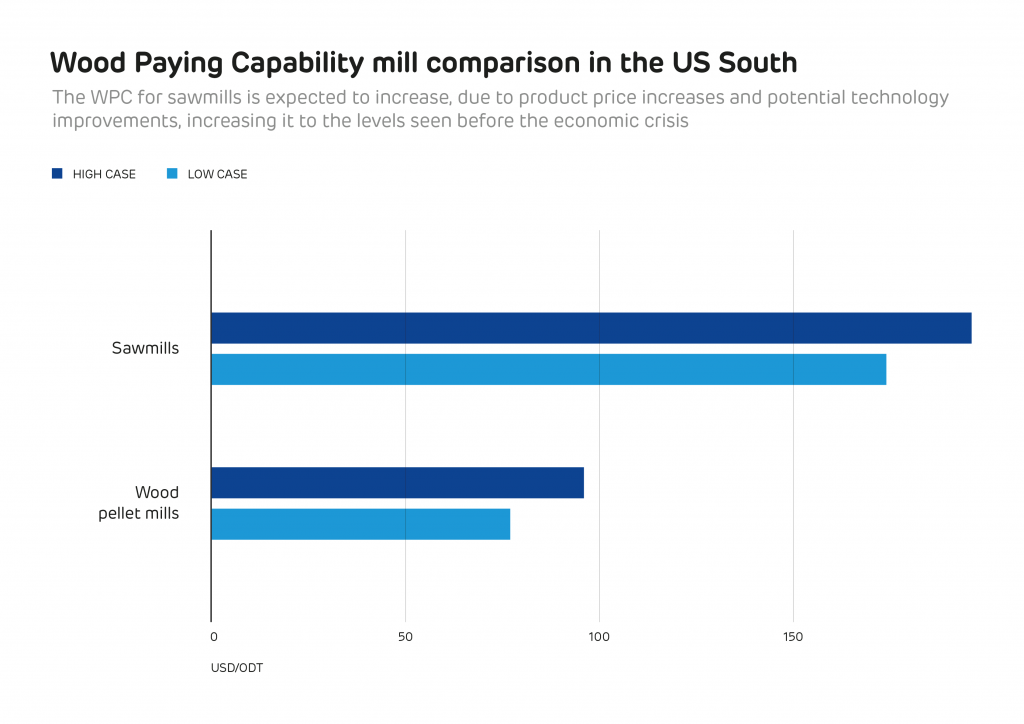
In the short-term, intelligence firm Hawkins Wright estimates global demand will increase by almost 30% during 2018 to reach 20.4 Mt, while Forisk predicts a smaller jump: an almost 5 Mt increase compared to 2017.
Most of this will continue to come from Europe (73% of global demand by 2021, more than 80% in 2018), where projects such as Lynemouth Power Station’s conversion from coal to biomass, as well as five co-firing units in the Netherlands are all set to come online very soon. While smaller in number, Asia is also developing a growing appetite for biomass and in 2018 demand is forecast to grow by 1.98 Mt.
These estimates might paint a picture of a continually soaring demand, but Forisk’s forecast actually expect this growth to plateau, levelling off around 2023 at 27.5 Mt. Hawkins Wright expects a similar slow down, forecasting manageable growth of under 15% between 2023 and 2026.
A forestry specialist at Drax Group, believes this plateau could come even sooner.
“Current and future forecasts in industrial wood pellet demand are based on a series of planned conversions and projects coming online,” he explains.
“But once these projects are active, demand in Europe will likely plateau around 2021 and then gradually reduce as various EU support schemes for industrial biomass come to an end. Any long term use of biomass is likely to be based on agricultural residues and wastes.”
But even with this expected slowdown, the biomass demand of the near future will be substantially higher than it is right now. So, the question remains, can suppliers meet the need for biomass pellets?

Meeting this growing demand depends on two factors: sufficient raw materials and the production capabilities to turn those materials into biomass pellets.
In today’s market, there’s no shortage of raw materials and low grade fibre. Instead, what could cause challenges is the production of pellets.
Hawkins Wright reports the capacity for global industrial pellet production was roughly 21.4 Mt a year at the end of 2017 and will increase by a further 3 Mt by 2019 as facilities currently under construction reach completion.
It means that to meet even Forisk’s conservative 27.5 Mt prediction by 2023, pellet production needs to increase. However, Drax’s forestry specialist points to the three to four years needed to complete pellet facilities and the relatively short period of time financial support programmes will remain in place as something that could lead to a slowdown in new plants coming online. Instead, he says, expansions of existing plants and the increased use of small-scale facilities will become crucial to increasing overall production.
However the biomass market changes and develops, it remains critical that proper regulation is in place, efficiencies are found and that technological innovation continues within the forestry industry so forests are grown and managed sustainably.
As we move into a low-carbon future we know that biomass demand will increase. But for this to be truly beneficial and sustainable we need to ensure we are not only meeting the demand of today but also of tomorrow, the day after tomorrow and beyond.
[1] Source: FAOSTAT
[2] Source: Hawkins Wright, The Outlook for Wood Pellets, Q4 2017
[3] https://www.forisk.com/blog/2015/10/23/nibbling-on-a-chicken-or-nibbling-on-an-elephant-another-example-of-incomplete-and-misleading-analysis-of-us-forest-sustainability-and-wood-bioenergy-markets/

Drax Biomass conducts regional risk assessments with extensive reviews of existing public and private datasets to identify high conservation value forests. This regional information is then augmented by county-level Natural Heritage data.
In 2017, Drax Biomass contracted with Nature Serve to package this regional- and county-level data into a format that would facilitate a rapid risk assessment for all in-woods fibre. This operational risk assessment procedure, combined with formal conservation commitments such as the Atchafalaya Basin Keeper agreement, reflect a comprehensive strategy to protect biodiversity.
Drax Biomass is looking forward to actively contributing to regional conservation enhancement efforts in 2018 and beyond.
A partnership formed with the American Forest Foundation (AFF) in 2017 is paving the way. The AFF is a publicly supported not-for-profit organization established to conduct charitable, educational, research and scientific programmes aimed at the responsible use and conservation of renewable resources. Our partnership with the AFF is aimed at improving habitat for at-risk southern wildlife species through active forest management. With open-canopy pine habitat identified as a conservation need, the market that Drax Biomass provides for small-diameter forest thinning material can directly benefit the regional biodiversity.
In addition to efforts around our own facilities, Drax Biomass employees have been contributing to a collaborative effort run by the Sustainable Biomass Program (SBP) to provide better information on how to assess whether or not there are forests with high conservation values in a catchment, and what to do about them. SBP expects to publish the guidance from this workgroup in early 2018.
In 2013, Drax co-founded the SBP together with six other energy companies.
SBP builds upon existing forest certification programmes, such as the Sustainable Forest Initiative (SFI), Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC). These evidence sustainable forest management practices but do not yet encompass regulatory requirements for reporting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This is a critical gap for biomass generators, who are obligated to report GHG emissions to European regulators.
There is also limited uptake of forest-level certification schemes in some key forest source areas. SBP is working to address these challenges.
SBP certification provides assurance that woody biomass is supplied from legal and sustainable sources and that all regulatory requirements for the users of biomass for energy production are met. The tool is a unique certification scheme designed for woody biomass, mostly in the form of wood pellets and wood chips, used in industrial, large-scale energy production.
SBP certification is achieved via a rigorous assessment of wood pellet and wood chip producers and biomass traders, carried out by independent, third party certification bodies and scrutinised by an independent technical committee.

A study on the historical trends in the forest industry of the US South, carried out by supply chain consultancy Forest2Market, and commissioned by Drax Group, the National Alliance of Forest Owners and the U.S. Endowment for Forestry and Communities, found that over the last 60 years, as demand for forestry products has increased, the productivity of the area’s forests has increased too. In short, the more we’ve come to use them, the more forests have grown.
A forest is not like a mine – there is not a finite amount of wood in the ground that disappears when it is extracted, never to return. Forests are a renewable resource that can be replanted, improved, and harvested for as long as the land is managed responsibly.
What’s more, landowners have a strong financial incentive to not only maintain their holdings but to improve their productivity – after all, the more of something you have, the more of it you have to sell. It is an economic incentive that works.
The Forest2Market report found that increased demand for wood is statistically correlated with more annual tree growth, more wood volume available in the forest, and more timberland.
For example, between 1953 and 2015, tree harvests increased by 57%, largely driven by US economic growth and increased construction. Over the same period, annual wood growth increased by 112%, and inventory increased by 108%. In total, annual growth exceeded annual removals by 38% on average.
Annual forest growth in the US South increased from 193 million cubic metres in 1953 to 408 million cubic metres in 2015. Inventory increased from 4 billion to 8.4 billion cubic metres.
The forest products industry funded private-public research projects to enhance the quality and performance of seedlings and forest management practices to ensure a stable supply of wood. Because of these efforts, landowners saw the value of active management techniques, changing their approach to site preparation, fertilization, weed control, and thinning, and the use of improved planting stock. Healthy demand made it easy for landowners to take a long-term view, investing in more expensive management practices up front for greater returns in the future. And the results were extraordinary: seedlings established in the last 20 years have helped plantations to become nearly four times as productive as they were 50 years ago.
Markets for wood have changed over the last two decades, precipitated by decreased demand for writing paper and newsprint, increased demand for absorbent hygiene products and containerboard and increased demand for biomass. These changes in demand have not impacted the way that landowners manage timberland, however. As sawtimber (the largest trees in the forest) remains the most valuable timber crop, it also remains the crop the landowners want to grow. Pulpwood is harvested from the forest only when the forest is being thinned to create optimal conditions for growing sawtimber or when sawtimber is harvested and the forest is being cleared for replanting.
Pellet production has expanded rapidly in the US South, though its overall footprint is still small in comparison to more traditional forest product industries.
In some local wood basins, however, like the one surrounding Bastrop, Louisiana (the location of one of Drax’s US production facilities), the use of biomass to create pellets has filled a gap left by the closure of an 80-year old paper mill. Drax’s decision to locate in this area is integral to supporting forest industry jobs and landowners who carefully consider local demand when deciding whether to continue growing trees.
According to Tracy Leslie, Director of Forest2Market’s biomaterials and sustainability practice, “As history has shown, forests in the US South have benefitted from increased demand for all types of wood. The rise of the pulp and paper industry did not detract from landowner objectives to maximize production of higher value sawtimber nor did it result in a shift in focus to growing only pulpwood. This new demand did, however, provide landowners with important interim and supplemental sources of income. Forest2Market’s research shows that an increase in demand for pellets will have the same effect, incentivizing landowners to grow and re-grow forests, increasing both forest inventory and carbon storage.”

Not only does demand for forest products increase the productivity and carbon storage of forests and provide an incentive for landowners to continue growing trees, but it also helps counter factors that irrevocably destroy this natural resource. The real threat to forests in the US is not demand for wood, but urbanisation. Nearly half of all US forestland that converted to another use between 1982 and 2012 was cleared for urban development.
Commercial forestry protects forested lands from development; between 1989 and 1999, just 1% of managed pine plantations in the US South were cleared for non-forest development compared to 3% of naturally-regenerated forest types.
Urbanisation, not the forest products industry, places the most pressure on forests in the US South. Forest2Market’s findings demonstrate that demand associated with healthy timber markets promotes the productivity of forests and mitigates forest loss by encouraging landowners to continue to grow, harvest, and regenerate trees.
Read the full report: Historical Perspective on the Relationship between Demand and Forest Productivity in the US South. An At A Glance version plus an Executive Summary are also available as a separate documents.

Read here
A truck arrives at an industrial facility deep in the expanding forestland of the south-eastern USA. It passes through a set of gates, over a massive scale, then onto a metal platform.
The driver steps out and pushes a button on a nearby console. Slowly, the platform beneath the truck tilts and rises. As it does, the truck’s cargo empties into a large container behind it. Two minutes later it’s empty.
This is how you unload a wood fuel truck at Drax Biomass’ compressed wood pellet plants in Louisiana and Mississippi.
“Some people call them truck dumpers, but it depends on who you talk to,” says Jim Stemple, Senior Director of Procurement at Drax Biomass. “We just call it the tipper.” Regardless of what it’s called, what the tipper does is easy to explain: it lifts trucks and uses the power of gravity to empty them quickly and efficiently.
The sight of a truck being lifted into the air might be a rare one across the Atlantic, however at industrial facilities in the United States it’s more common. “Tippers are used to unload trucks carrying cargo such as corn, grain, and gravel,” Stemple explains. “Basically anything that can be unloaded just by tipping.”
Both of Drax Biomass’ two operational pellet facilities (a third is currently idle while being upgraded) use tippers to unload the daily deliveries of bark – known in the forestry industry as hog fuel, which is used to heat the plants’ wood chip dryers – sawdust and raw wood chips, which are used to make the compressed wood pellets.
The tipper uses hydraulic pistons to lift the truck platform at one end while the truck itself rests against a reinforced barrier at the other. To ensure safety, each vehicle must be reinforced at the very end (where the load is emptying from) so they can hold the weight of the truck above it as it tips.
Each tipper can lift up to 60 tonnes and can accommodate vehicles over 50 feet long. Once tipped far enough (each platform tips to a roughly 60-degree angle), the renewable fuel begins to unload and a diverter guides it to one of two places depending on what it will be used for.
“One way takes it to the chip and sawdust piles – which then goes through the pelleting process of the hammer mills, the dryer and the pellet mill,” says Stemple. “The other way takes it to the fuel pile, which goes to the furnace.”
The furnace heats the dryer which ensures wood chips have a moisture level between 11.5% and 12% before they go through the pelleting process.
“If everything goes right you can tip four to five trucks an hour,” says Stemple. From full and tipping to empty and exiting takes only a few minutes before the trucks are on the road to pick up another load.
Using the power of gravity to unload a truck might seem a rudimentary approach, but it’s also an efficient one. Firstly, there’s the speed it allows. Multiple trucks can arrive and unload every hour. And because cargo is delivered straight into the system, there’s no time lost between unloading the wood from truck to container to system.
Secondly, for the truck owners, the benefits are they don’t need to carry out costly hydraulic maintenance on their trucks. Instead, it’s just the tipper – one piece of equipment – which is maintained to keep operations on track.
However, there is one thing drivers need to be wary of: what they leave in their driver cabins. Open coffee cups, food containers – anything not firmly secured – all quickly become potential hazards once the tipper comes into play.
“I guess leaving something like that in the cab only happens once,” Stemple says. “The first time a trucker has to clean out a mess from his cab is probably the last time.”
Can you count the number of trees in the world? Accurately, no – there are just too many, spread out over too vast an area. But if we could, what would we gain? For one, we would get a clearer picture of what’s happening in our planet’s forests.
They’re a hugely important part of our lives – not only for the resource they provide, but for their role in absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2). So properly understanding their scale and what is happening to them – whether increasing or decreasing – and designing strategies to manage this change is hugely important.
The trouble is, they exist on such a vast scale that we traditionally haven’t been able to accurately monitor them en masse. Thanks to space technologies, that’s changing.

As far back as World War II, aerial imaging was being used to monitor the environment. In addition to using regular film cameras mounted to aeroplanes to follow troops on the ground, infrared film was used to identify green vegetation and distinguish it from camouflage nets.
As satellite and remote sensing technology developed through the 20th century, so too did our understanding of our planet. Satellites were used to map the weather, monitor the sea, and to create topological maps of the earth, but they weren’t used to track the Earth’s forests in any real detail.
But in 2021 the European Space Agency (ESA) will launch Biomass, a satellite that will map the world’s forests in unprecedented detail using the first ever P-band radar to be placed in Earth orbit. This synthetic aperture radar penetrates the forest canopy to capture data on the density of tree trunks and branches. It won’t just be able to track how much land a forest covers, but how much wood exists in it. In short, the Biomass will be able to ‘weigh’ the world’s forests.
Over the course of its five-year mission, it will produce 3D maps every six months, giving scientists data on forest density across eight growth cycles.
The satellite is part of ESA’s Earth Explorers programme, which operates a number of satellites using innovative sensor technology to answer environmental questions. And it’s not the only entity carrying out research of this sort.
California-based firm Planet has 149 micro-satellites measuring just 10cm x 30cm in orbit around the Earth, each of which beams back around three terabytes of data every day. To put it another way, each satellite photographs about 2.5 million square kilometres of the Earth’s surface on a daily basis.
The aim of capturing this information is to provide organisations with data to help them answer the question: what is changing on Earth? When it comes to forests, this includes identifying things like illegal logging and forest fires, but the overall aim is to create a searchable, expansive view of the world that enables people to generate useful insights.
All this data is not only vital for developing our understanding of how the world is changing, it is vital for the development of responsible, sustainable forestry practices.
From 2005 to 2015, the UN rolled out the REDD programme (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation), which, among other functions, allows countries to earn the right to offset CO2 emissions – for example through forestry management practices. Sophisticated satellite measurement techniques not only let governments know the rate of deforestation or afforestation in their respective countries, it can also help them monitor, highlight and encourage responsible forestry.
Satellite technology is increasingly growing the level of visibility we have of our planet. But more than just a clearer view on what is happening, it allows us the opportunity to see why and how it is happening. And it’s with this information that real differences in our future can be made.

Bioenergy is the world’s largest renewable energy source, providing 10% of the world’s primary supply. But more than just being a plentiful energy source, it can and should be a sustainable one. And because of this, it’s also a focus for innovation.
Biomass currently powers 4.8% of Great Britain’s electricity through its use at Drax Power Station and smaller power plants, but this isn’t the only way bioenergy is being used. Around the world people are looking into how it can be used in new and exciting ways.
 Powering self-sufficient robots
Powering self-sufficient robots Algae and microscopic animals
To power two aquatic robots with mouths, stomachs and an animal-type metabolism. Designed at the University of Bristol, the 30cm Row-Bot is modelled on the water boatman insect. The other, which is smaller, closer resembles a tadpole, and moves with the help of its tail.
Both are powered by microbial fuel cells – fuel cells that use the activity of bacteria to generate electricity – developed at the University of the West of England in Bristol. As they swim, the robots swallow water containing algae and microscopic animals, which is then used by their fuel cell ‘stomachs’ to generate electricity and recharge the robots’ batteries. Once recharged, they row or swim to a new location to look for another mouthful.
It’s hoped that within five years the Row-Bot will be used to help clean up oil spills and pollutants such as harmful algal bloom. There are plans to reduce the tadpole bot to 0.1mm so that huge shoals of them can be dispatched to work together to tackle outbreaks of pollutants.
 Purifying water
Purifying waterHuman waste
The Omni Processor, a low cost waste treatment plant funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, does something incredible: it turns sewage into fresh water and electricity.
It does this by heating human waste to produce water vapour, which is then condensed to form water. This water is passed through a purification system, making it safe for human consumption. Best of all, it does this while powering itself.
The solid sludge left over by the evaporated sewage is siphoned off and burnt in a steam engine to produce enough electricity to process the next batch of waste.
The first Omni Processor was manufactured by Janicki Bioenergy in 2013 and has been operating in Dakar, Senegal, since May 2015. A second processor, which doubles the capacity of the first, is currently operating in Sedro-Woolley, Washington, US and is expected to be shipped to West Africa during 2017.
Closer to home and Drax Power Station, a similar project is already underway. Northumbrian Water was the first in the UK to use its sludge to produce renewable power, but unlike the Omni Processor, it uses anaerobic digestion to capture the methane and carbon dioxide released by bacteria in sludge to drive its gas turbines and generate power. Any excess gas generated is delivered back to the grid, resulting in a total saving in the utility company’s carbon footprint of around 20% and also multi-millions of pounds of savings in operating costs.
 Flying across the Atlantic
Flying across the AtlanticTobacco
Most tobacco is grown with a few factors in mind – taste and nicotine content being the most important. But two of the 80 acres of tobacco grown at Briar View Farms in Callands, Virginia, US, are used to grow tobacco of a very different sort. This tobacco can power aeroplanes.
US biofuel company Tyton BioEnergy Systems is experimenting with varieties of tobacco dropped decades ago by traditional growers because of poor flavour or low nicotine content. The low-nicotine varieties need little maintenance, are inexpensive to grow and flourish where other crops would fail.
The company is turning this tobacco into sustainable biofuel and last year filed a patent for converting oil extracted from plant biomass into jet fuel.
In the hope of creating a promising source of renewable fuel, scientists are pioneering selective breeding techniques and genetic engineering to increase tobacco’s sugar and seed oil content.
In 2013, the US Department of Energy gave a $4.8m grant to the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, in partnership with UC Berkeley and the University of Kentucky, to research the potential of tobacco as a biofuel.
Wood exposed to radiation by the Fukushima nuclear meltdowns
Last year it was announced that German energy company Entrade Energiesysteme AG, will set up biomass power generators in the Fukushima prefecture that will generate electricity using the lightly irradiated wood of the area.
It’s hoped they will help Japan’s attempts to repopulate the region following the 2011 earthquake, tsunami and nuclear accident. Entrade says its plants can reduce the mass of lightly irradiated wood waste by 99.5%, which could help Japanese authorities reduce the amount of contaminated material while at the same time generating sustainable energy.
The prefecture aims to generate all its power from renewable energy by 2040 through a mix of bioenergy and solar power.